types of vaccine delivery system
This is to stimulate the immune response to recognise a pathogen a disease-causing organism or part of a pathogen. We will discuss each of these briefly in the following slides.
Subunit recombinant conjugate and polysaccharide vaccines.

. Topics to be addressed include ensuring the safety and efficacy of Covid-19 vaccines principles for vaccine allocation strategies for deployment and delivery of Covid-19 vaccines vaccine. Another type of vaccine is a subunit vaccine which is made from proteins found on the surface of infectious agents. The vaccine delivery options available may also differ geographically.
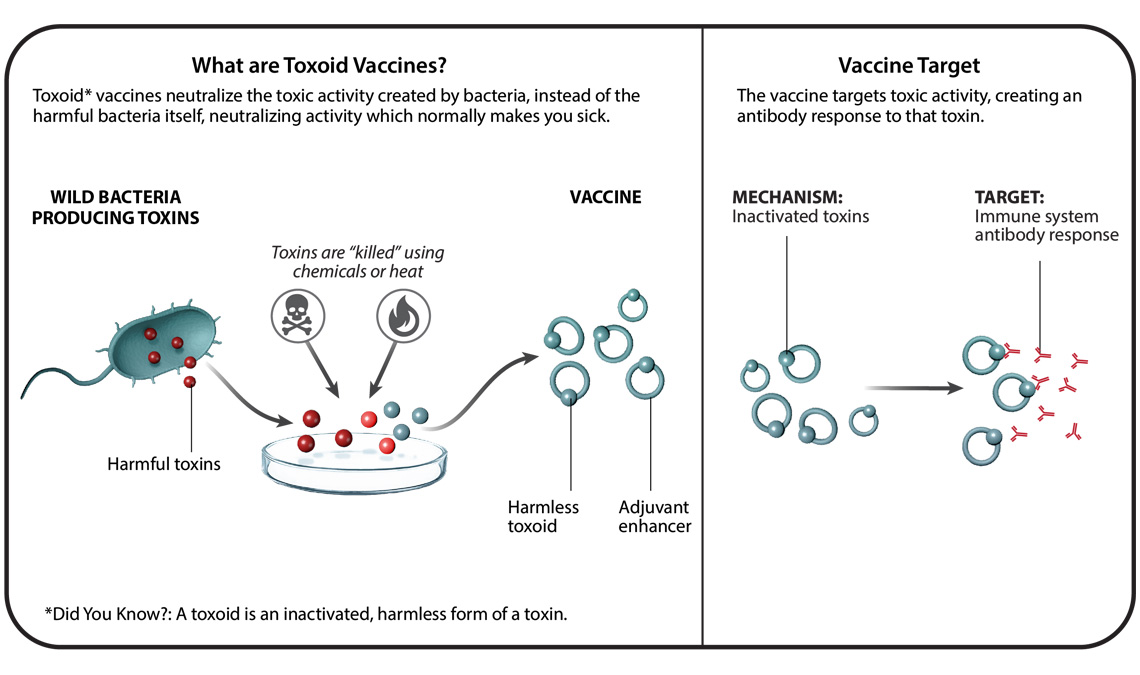
The features modes of viral entry and replication expression of heterologous proteins. Toxoid inactivated toxin Diphtheria tetanus part of DTaP combined immunization. 1 WHOLE VIRUS VACCINE.
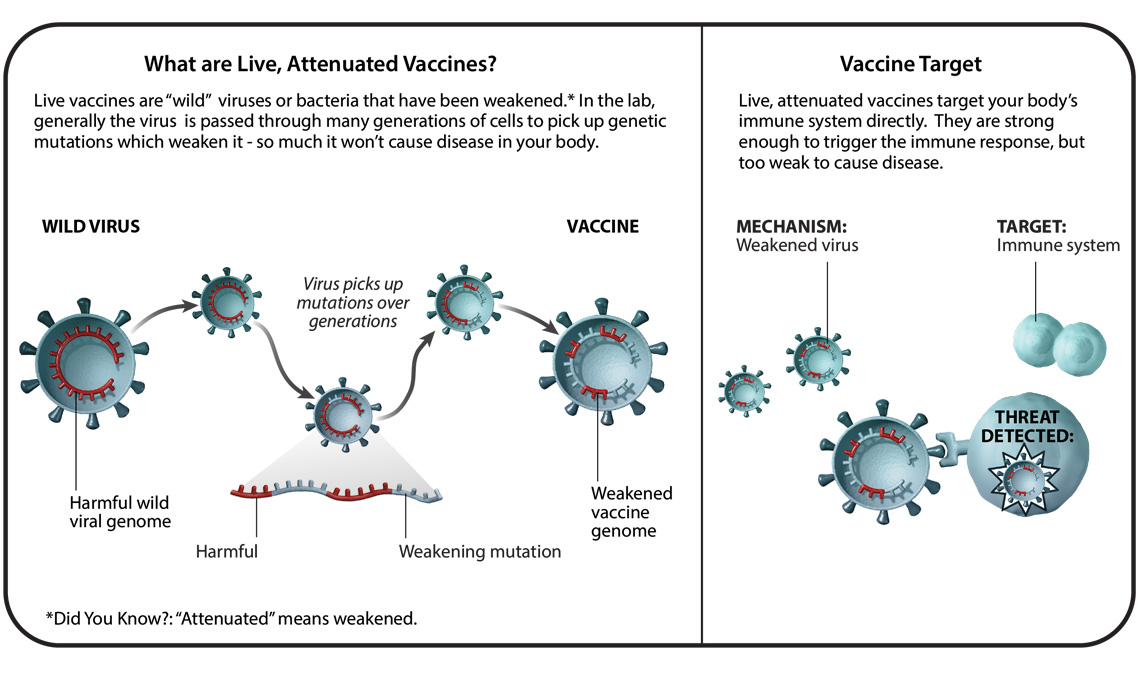
Live attenuated vaccines fight viruses and bacteria. Vaccines can be divided into a number of different types but ultimately work on the same principle. This photo shows a r esponder at an.
Delivery systems for mRNA vaccines can be divided into viral- and non-viral vector delivery systems. The preprint described Modernas coronavirus vaccine candidate as using delivery technology that appears to be covered in the Arbutus patent that was upheld last week. A vaccine delivery system is the means by which the immune-stimulating agent constituting the vaccine is packaged and administered into the human body to ensure that the vaccine reaches the desired tissue.
Or being studied include. These novel vaccination delivery systems offer several advantages over the injectable preparations including self-administration reduced cost stability and elimination of a cold. These vaccines contain a version of the living virus or bacteria that has been weakened so that it does not cause serious disease in people with.
Hepatitis A polio rabies all inactivated type. The key difference between the four main types of vaccines is the method of exposure used. This review discusses selected viral vector systems and plasmid DNA and provides an overview of their specific characteristics strengths and limitations.
The invention by Moyer describes methods and systems for generating a safe and effective oral smallpox vaccine for humans using a genetically defective strain of vaccinia virus to confer immunity following oral delivery of the vaccine. An mRNA vaccine or RNA vaccine is a novel type of vaccine which is composed of the nucleic acid RNA packaged within a vector such as lipid nanoparticles. New developments in vaccine delivery systems will improve the efficiency of clinical trials in the near future.
The size of the particle systems influences cellular targeting. Here are the key differences. Among them nanoparticles NPs such as dendrimers polymeric NPs metallic NPs magnetic NPs and quantum dots have emerged as effective vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases and cancer therapy.
Today there are five main types of vaccines that infants and young children commonly receive in the US. After vaccination your muscle cells begin making the S protein pieces and. The intended audience is the general public as well as policymakers educators and key stakeholders interested in a concise guide to Covid-19 vaccines.
The main types of COVID-19 vaccines currently available in the US. While microneedles were initially explored for transdermal drug delivery applications their use has been extended for the intraocular vaginal transungual cardiac vascular gastrointestinal and intracochlear delivery. In particular novel strategies based on edible or intradermal vaccine formulations have been demonstrated to trigger both a systemic and mucosal immune response.
Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles microparticles or adjuvant-formulated proteins. Among the COVID-19 vaccines are a number of RNA vaccines under development to combat the COVID-19 pandemic and some have been approved or have received emergency use authorization in some countries. The vaccine invention can be delivered as a live virus with the ability to express viral proteins but unable to achieve complete lytic virus.
Once the immune system has been trained to recognise this if the body is later exposed to the pathogen it will be removed from the body. This approach uses similar technology to the inactivated vaccine and can be manufactured at scale. They have tested the delivery system in mice achieving a remarkable success delivering drugs to tumors.
Recommended Childhood ages 0-6 Immunization Schedule. Besides simply being compatible with any type of vaccines including the mRNA DNA protein subunit and live attenuated vaccines microneedles are also advantageous because they could replace traditional large needles in parts of the world with a high burden of HIV and other diseases. COVID-19 vaccines protect against COVID-19.
Live-attenuated vaccine. Microneedles or Microneedle Patches or Microarray Patches are micron-scaled medical devices used to administer vaccines drugs and other therapeutic agents. The common routes of vaccine delivery are parenteral injection needle-free injections intranasal ocular oral and spray topical.
This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give your cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the COVID-19 virus. Number of doses required. A live-attenuated vaccine uses a living but weakened version of the virus or one thats very similar.
Other NIBIB-funded researchers are developing a system of drug delivery using a type of bacteria that has a two-part navigation systemmagnetic and oxygen sensing. Vaccines of this type on US. CDC is using IT systems to collect data about how many doses of COVID-19 vaccines have been delivered and how many doses have been administered.
Polio IPV Hepatitis A. Measles mumps rubella MMR combined vaccine Varicella chickenpox Influenza nasal spray Rotavirus. The main types of vaccines that act in different ways are.
Messenger RNA mRNA vaccine. The preprint of the study. The bacteria seek out oxygen-poor zones which are a feature of tumors.
Get safety info and more. This review mainly discusses non-viral vectors which can be further subdivided into lipid or lipid materials and polymer delivery systems. Other licensed vaccines that use this type of technology.
Viral vectors have different capabilities as gene delivery vehicles for vaccines and immunotherapeutics. The measles mumps and rubella MMR vaccine and the chickenpox and shingles vaccine are examples of this type of vaccine.
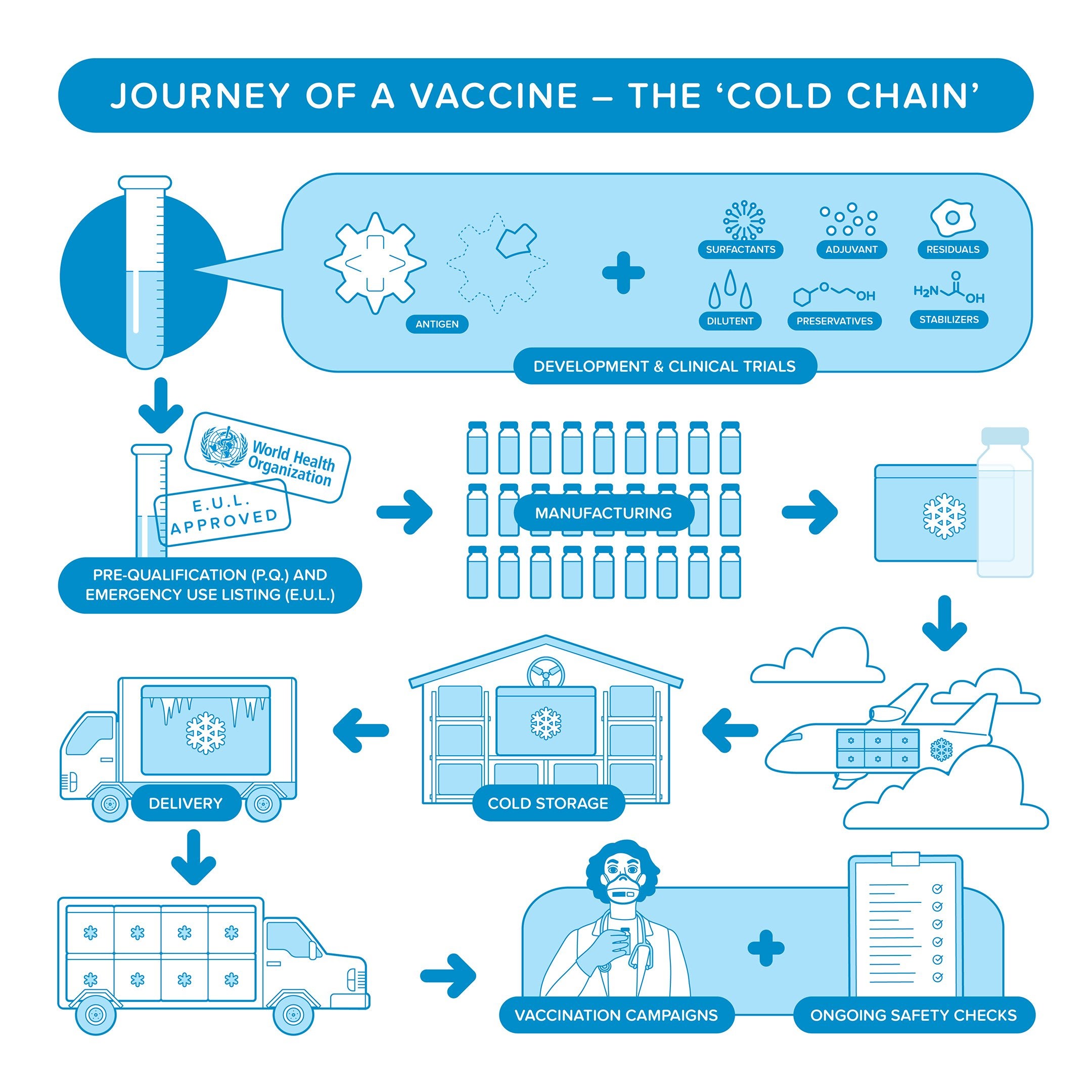
Cold Chain Paho Who Pan American Health Organization
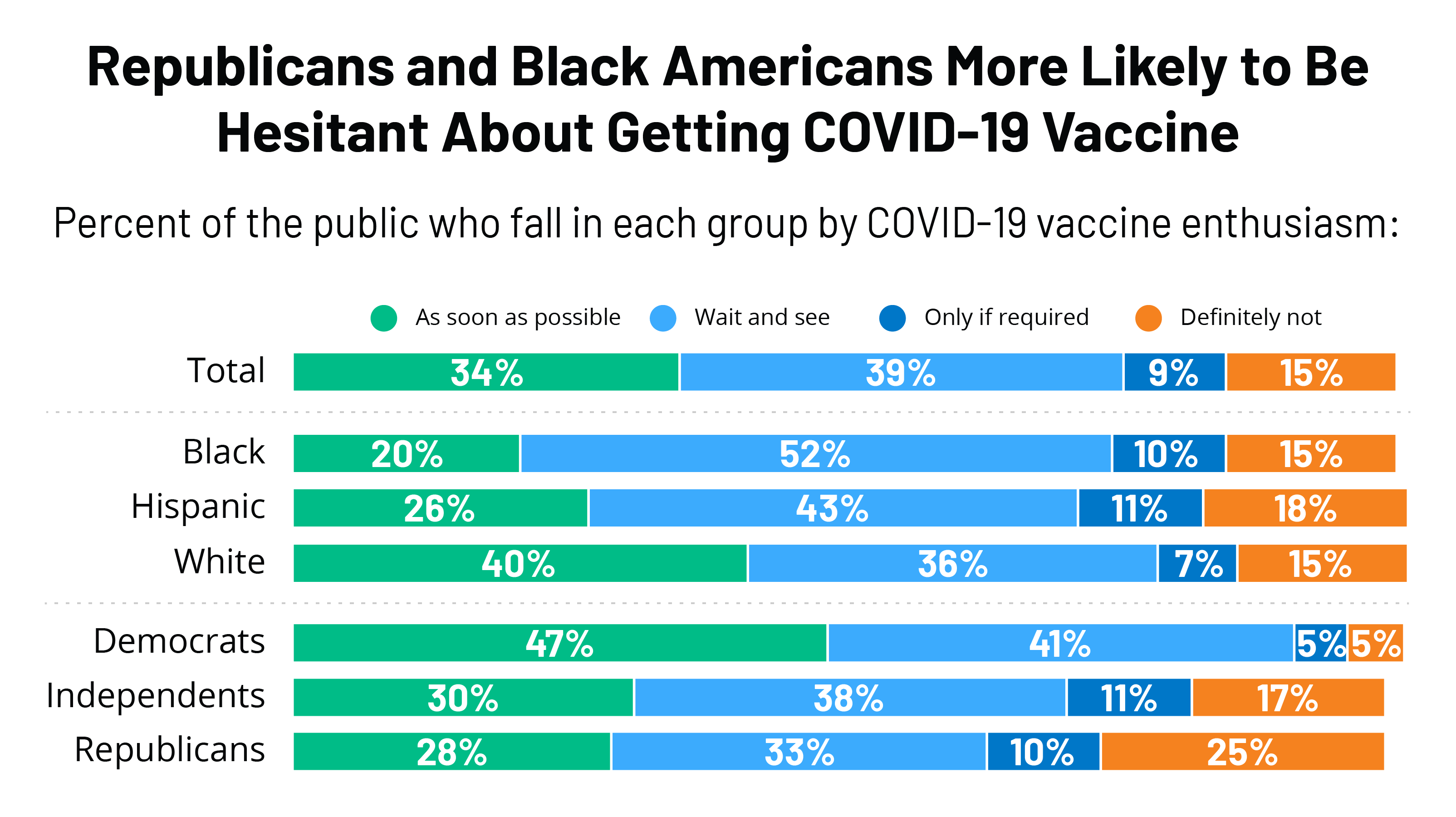
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff
What Are Viral Vector Based Vaccines And How Could They Be Used Against Covid 19 Gavi The Vaccine Alliance
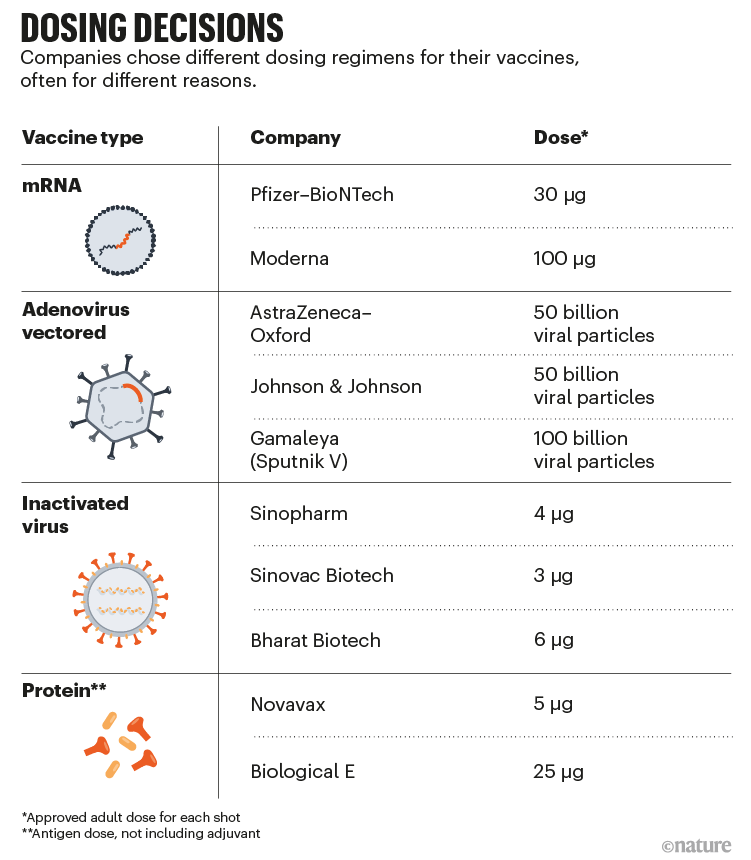
Could Computer Models Be The Key To Better Covid Vaccines

How The Oxford Astrazeneca Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times
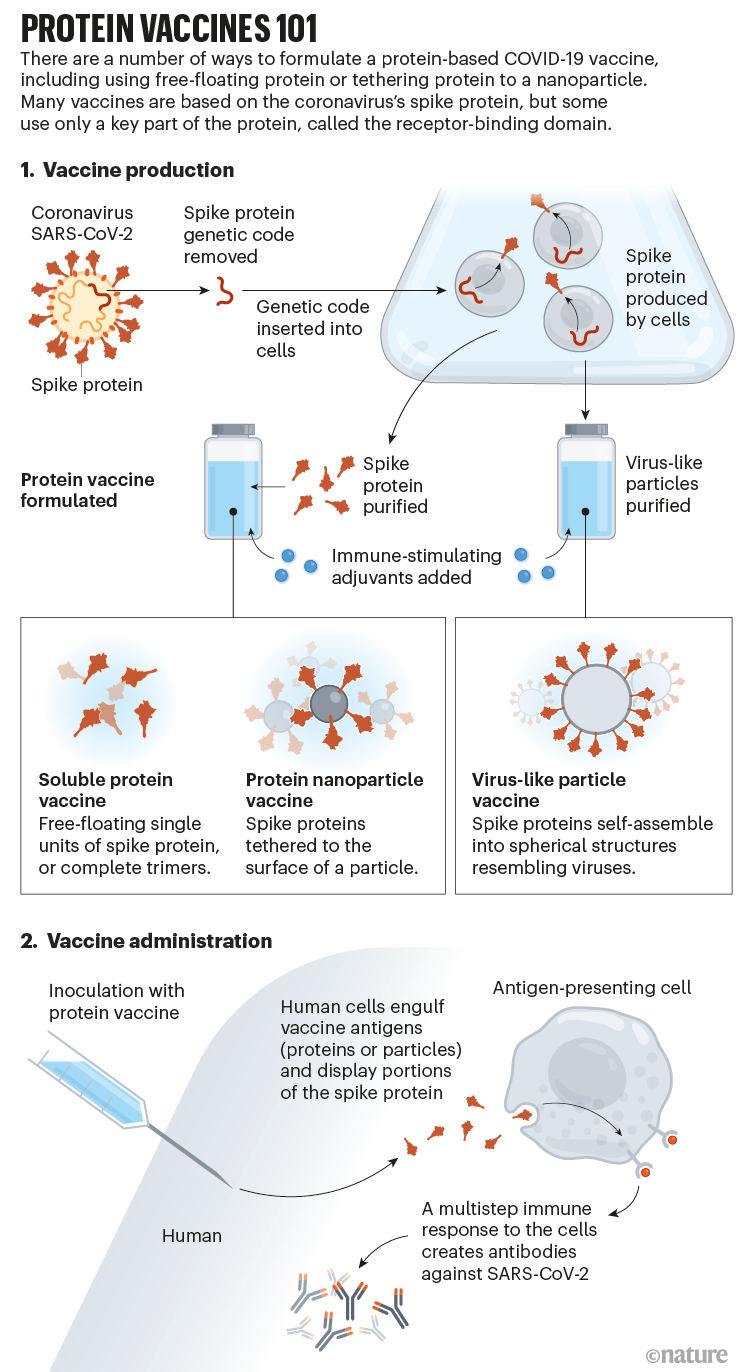
How Protein Based Covid Vaccines Could Change The Pandemic

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine

Forward Of Targeted Drug Delivery Jmdh Jmdh

Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times

All Types Of Covid 19 Vaccines How They Work Animation Youtube
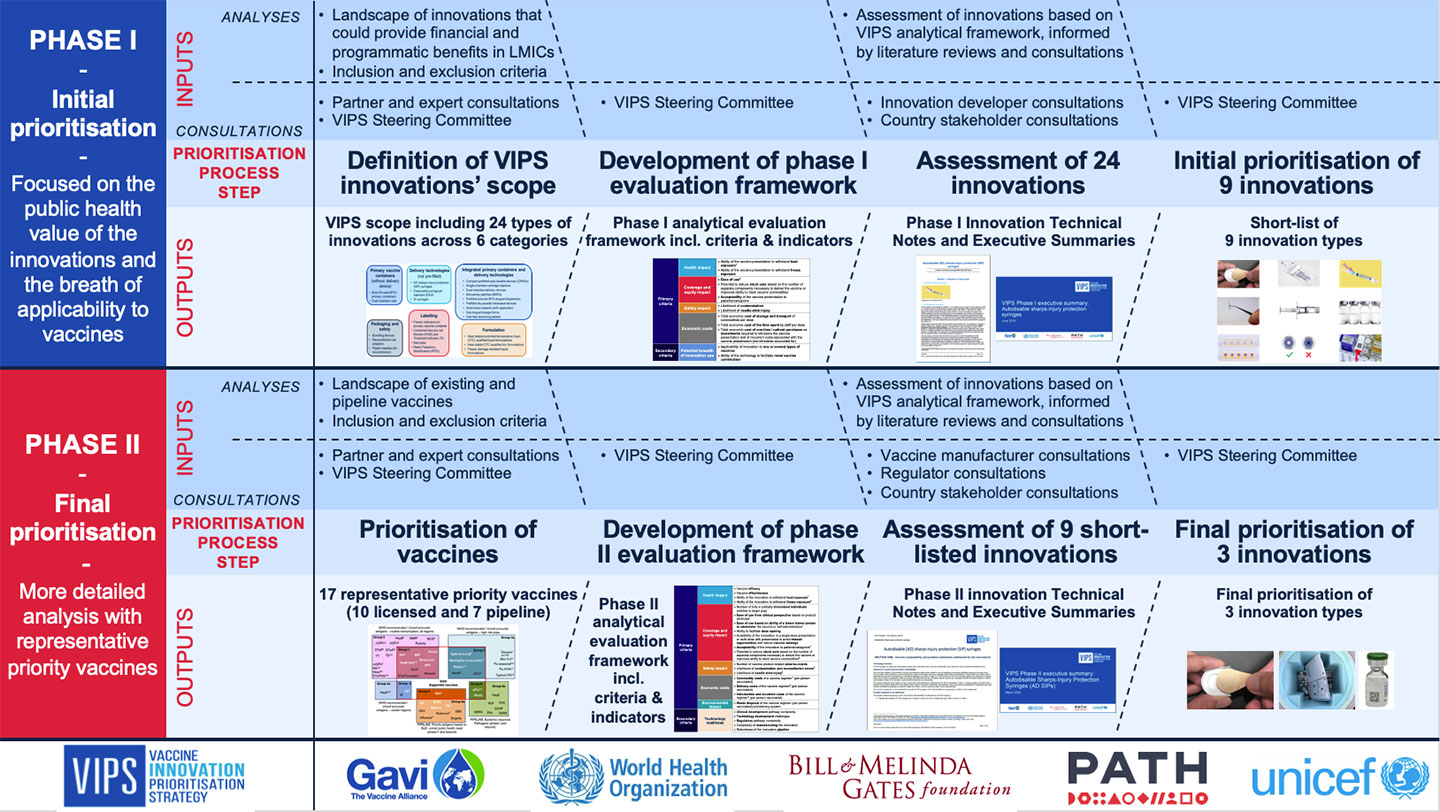
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
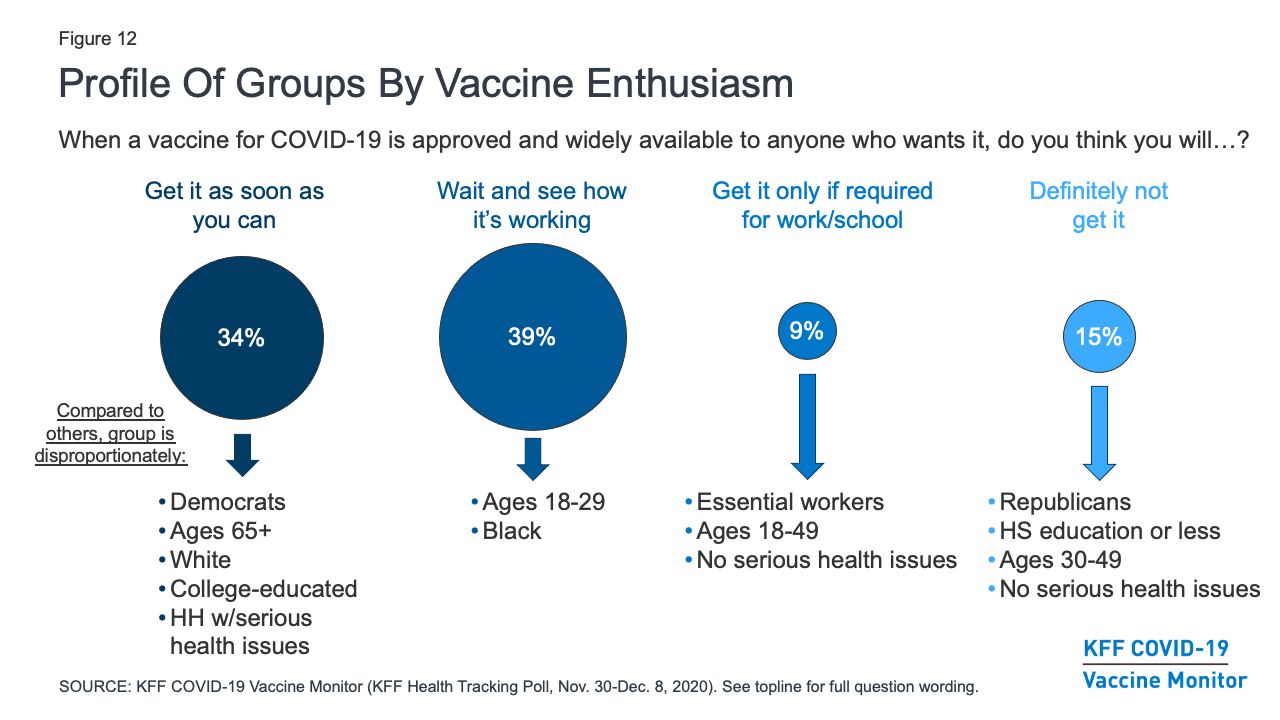
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff